While MCUs are becoming more powerful, machine learning models can be designed to utilize fewer resources. This enables the implementation of TinyML; deep learning models which can run on resource-constrained IoT devices. TinyML can be used to analyze raw sensor data locally which reduces or removes the need to send data to the cloud, lowers battery consumption, and preserves data privacy.
Nevertheless, implementing intelligent IoT solutions does not solely rely on the ML model itself. It involves challenges such as implementing continual learning, enabling low-power wireless communication, managing devices remotely, ensuring secure communication, updating the firmware (over the air), and enabling device interoperability.
“TinyML can be used to analyze raw sensor data locally which reduces or removes the need to send data to the cloud, lowers battery consumption, and preserves data privacy.”
-AVSystem
TinyML & LwM2M Complement Each Other
LwM2M is an application-layer communication standard that simplifies messaging and device management for IoT devices. The protocol dictates a data format and defines device management mechanisms and standardized processes for firmware-over-the-air updates (FOTA). The protocol is well-suited for LPWAN standards such as NB-IoT and LTE-M.
While TinyML provides the device intelligence (using tools such as Edge Impulse or Cartesiam.ai), the LwM2M protocol provides connectivity, standardized communication, and device management. When combined, they create a holistic solution for smart IoT devices.

Retrofitting Existing Devices with Smart Sensors
Cloud-based analysis of a device’s raw sensor data is inefficient due to the volume of data the device needs to transmit. A more efficient way is to process data from sensors directly on the device using TinyML. For example, analyzing the X, Y, and Z values of the accelerometer can detect complex movements or vibrations which could give valuable insights, enabling use cases such as predictive maintenance, monitoring the utilization of valuable goods, or classifying movements of people or animals.
These days, more and more smart sensors are being developed. In addition to their sensing capabilities, smart sensors come with an embedded MCU which runs the TinyML model and communicates only the detected patterns to the main MCU of the device. These TinyML integrated sensors are referred to as the Sensor 2.0 Paradigm by Prof. Vijay Janapa Reddi (Harvard University) during his recent lecture at the TinyML Summit. Smart sensors simplify the implementation of TinyML as it allows for retrofitting existing devices with TinyML capabilities without having to redesign the embedded firmware. In addition, it can solve privacy issues due to the true isolation of raw sensor data. Smart sensors can analyze voices or camera images while ensuring people’s privacy as data does not leak out to the main MCU of the device.
Continual Learning
One of today’s key challenges is to keep the TinyML model reliable post-deployment. Oftentimes, datasets used for training purposes differ from real-world data, leading to inaccurate models. In addition, the environmental context may change over time (e.g. due to the decalibration of industrial machines, or changing climate conditions) leading to the deterioration of the model quality.
Continual learning refers to the ability of TinyML models to adapt over time. This can be accomplished by learning from new data sets without the need to retrain the model from scratch. Although the techniques to realize continual learning are well-known, practical implementations are often missing when running the models on resource-constrained devices. Often, this has to do with a missing device-management layer that takes care of ML model lifecycle management. LwM2M may be the missing link to realize continual learning as it comes with native support for remote configurations and firmware updates. Using proven methods, ML models can be updated continuously without having to physically access each device to update its firmware.
TinyML Catalyst
TinyML solutions for resource-constrained IoT devices are a catalyst for the development of intelligent solutions. To move beyond the current POC phase and start deploying actual TinyML applications, it is necessary to provide mechanisms for efficient communication, device, and firmware management, and secure connectivity. The use of the LwM2M protocol to manage TinyML models and provide connectivity is a path towards standardizing TinyML and enriching the ecosystem of intelligent IoT solutions.
Case Study: TinyML Pattern Detector
A TinyML solution has been designed using the LwM2M standard. The Thingy:91 is a development device that uses the nRF9160 SiP from Nordic Semiconductor. It runs the Zephyr OS operating system and was trained to detect three different motion patterns, as shown in the visual below.
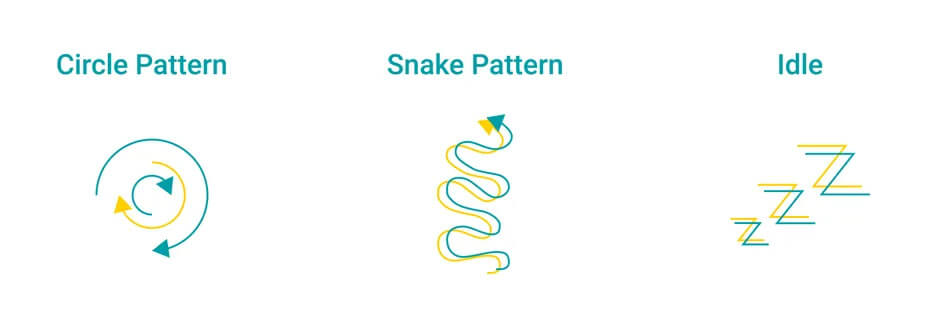
The steps to implement the presented concept are as follows:
- Data collection and labeling.
- Design and train the classifier.
- Deploy and test the classifier on the device.
- Provide network connectivity and device management by implementing an LwM2M client.
- Manage devices and data using an LwM2M server.
The example uses the Edge Impulse platform to collect the data from the Thingy:91 accelerometer, train the ML classifier, and generate standalone libraries for C++. The library containing the TinyML model can run on the device and control the LED signaling pattern detection. The Anjay LwM2M client provides a connectivity layer for the solution, handling low-level technology issues related to communication and secure data transmission.
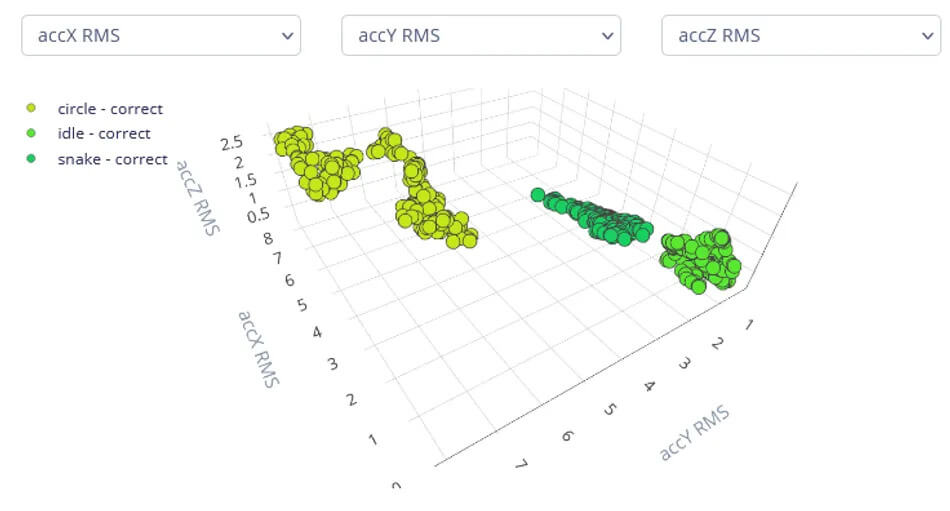
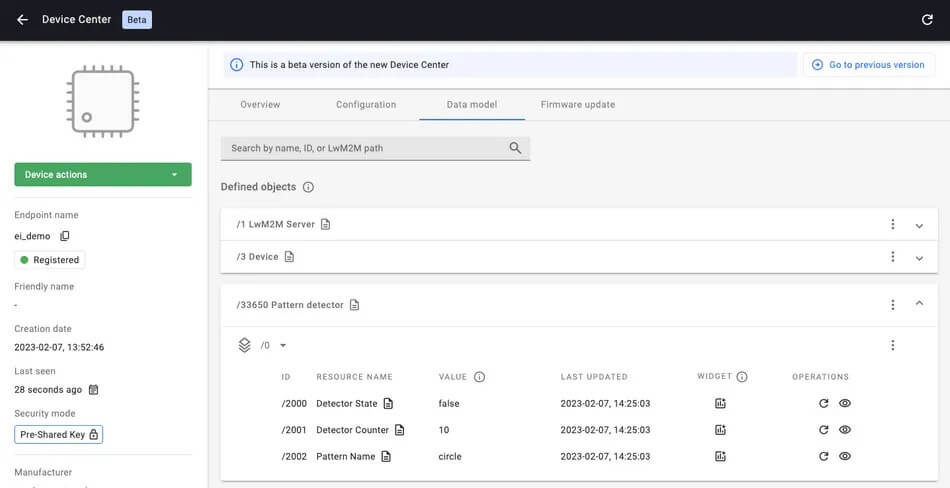
Finally, the device is registered in the LwM2M server where the data is stored and visualized. Using the Coiote IoT Device Management portal, the device can be instructed to notify the server every time a specific pattern is detected or to reduce the frequency to once every several seconds, minutes, or hours and send a counter indicating the number of times a pattern has been detected.
Tweet
Share
Share
- Automation
- Connectivity
- Internet of Things
- Machine Learning
- NB-IoT
- Automation
- Connectivity
- Internet of Things
- Machine Learning
- NB-IoT
