
Cellular IoT technology is an essential component of both 4G and 5G connectivity, providing Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) and Mobile Virtual Network Operators (MVNOs) with a foundation to enhance their digital capabilities. The embedded SIM (eSIM) delivers secure digital connectivity service and plays a crucial role in M2M connections with the ability to store multiple local network operator credentials and the capacity to be remotely provisioned over the air. Managing cellular IoT connectivity is made easier with eSIM, which enables ongoing technology improvements and continuous updates with mobile network operator profiles.
“Managing cellular IoT connectivity is made easier with eSIM, which enables ongoing technology improvements and continuous updates with mobile network operator profiles.”
MNO Profiles
At the heart of each connected IoT device is the Mobile Network Operator (MNO) profile. Profiles can be pre-loaded onto the embedded SIM (eSIM) or downloaded over the air after products are shipped to their global destinations. In the second scenario, enterprises can use business logic, configured within a connectivity orchestration platform, to define which network, and thus subscription profile, their devices should use to connect with.
Secure Device Management
The eUICC or software component allows for remote SIM provisioning and the ability for a connected device to switch between different network operators. Once a device is switched on, the eSIM updates with the most appropriate MNO profile over the Air using Remote SIM Provisioning (RSP) service. Also important to note is that profile data is protected at each point of the RSP process and digital certification is achieved on both the device and server side. Certification is only available by completing the GSMA certification.
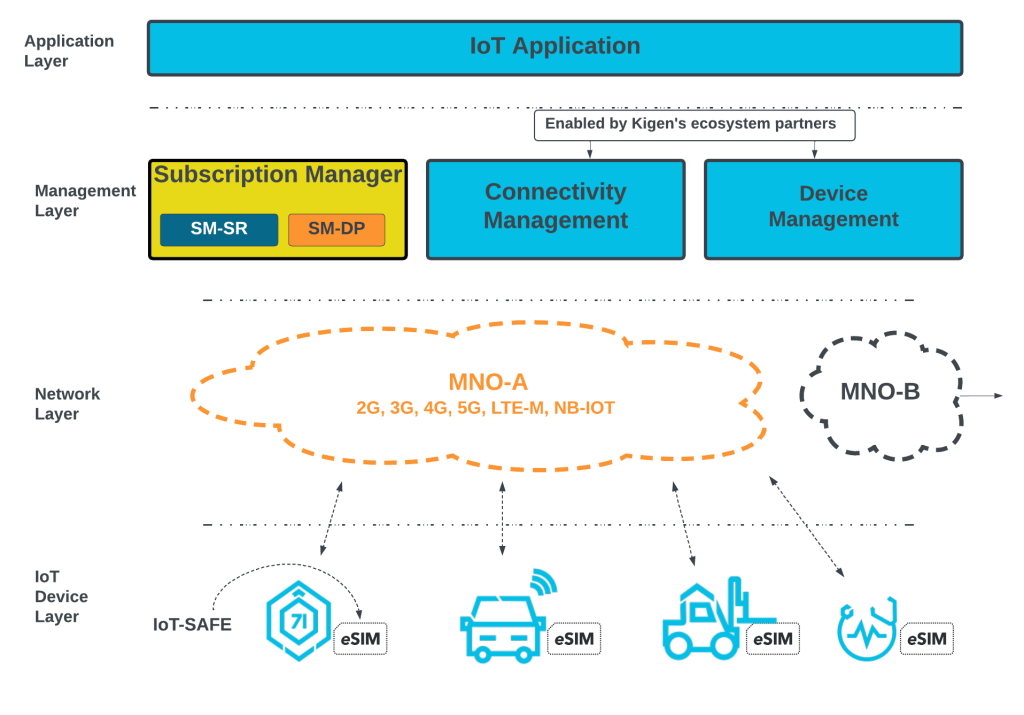
Connecting IoT Devices for the First Time
When an eSIM device is deployed in the field and connects for the first time, it uses a preloaded bootstrap profile that offers global connectivity options to connect to the cellular network. The bootstrap allows the device to connect straight out of the box to permitted networks within the coverage limitations and cellular technology the device supports. As soon as a profile is selected to switch to, it can be replaced by alternative operator profiles through remote SIM provisioning (RSP).
End-to-end communication between the device and IoT application must be secured; GSMA-standard IoT SAFE (Sim applet for Secure End-to-End) is well positioned to provide chip-to-cloud security using the SIM hardware root-of-trust. IoT SAFE favors TLS or DTLS technology and can be deployed on any SIM form factor: physical SIM, eSIM, and integrated SIM (iSIM).
Selecting the Right Cellular Technology
Selecting the right network connectivity depends on device location, security needs, coverage, data throughput, and budget. Your IoT requirements will define the best connectivity solution to ensure your organization is in control of smart data streams. It means having an in-depth understanding of your IoT applications and detailed knowledge of the tasks that need to happen at each deployment phase.
Here is a brief overview of some IoT connectivity options:
Fifth Generation Cellular Networks (5G)
5G is an emerging technology that is being rolled out globally. It provides up to 20Gbps, delivering more data than ever, and can support many devices in the same confined area. 5G offers low latency, meaning applications can run in near real-time and benefit from the ease of deployment and longevity with eSIM.
Sectors such as healthcare, security, automated transport, and industrial apps will benefit from greater reliability for faster analysis. Private 5G also provides the privacy, security, throughput, and control needed by oil and gas and industrial IoT enterprises. 5G, especially private 5G, in conjunction with Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN), can be leveraged for ubiquitous IoT connectivity in urban and remote areas.
Low-Power Wide-Area Networks (LPWAN)
LPWAN is a communication technology that uses low power consumption, low data rate, and wide-area coverage, perfectly suitable for many IoT and M2M applications such as smart cities, logistics tracking, and related industries. The connectivity and operational cost are typically lower than conventional cellular systems.
Licensed LPWAN runs on public cellular networks which support the GSM 3GPP standard and includes over 1000 global mobile operators who adhere to the standard. This connectivity technology is ideal for devices that only need to send small amounts of data periodically and use battery-powered devices that must last many years. IoT devices using this technology periodically send small packets of data, such as updates and reports. The advantages of LPWAN include low hardware costs, long-range connectivity, and extended battery life.
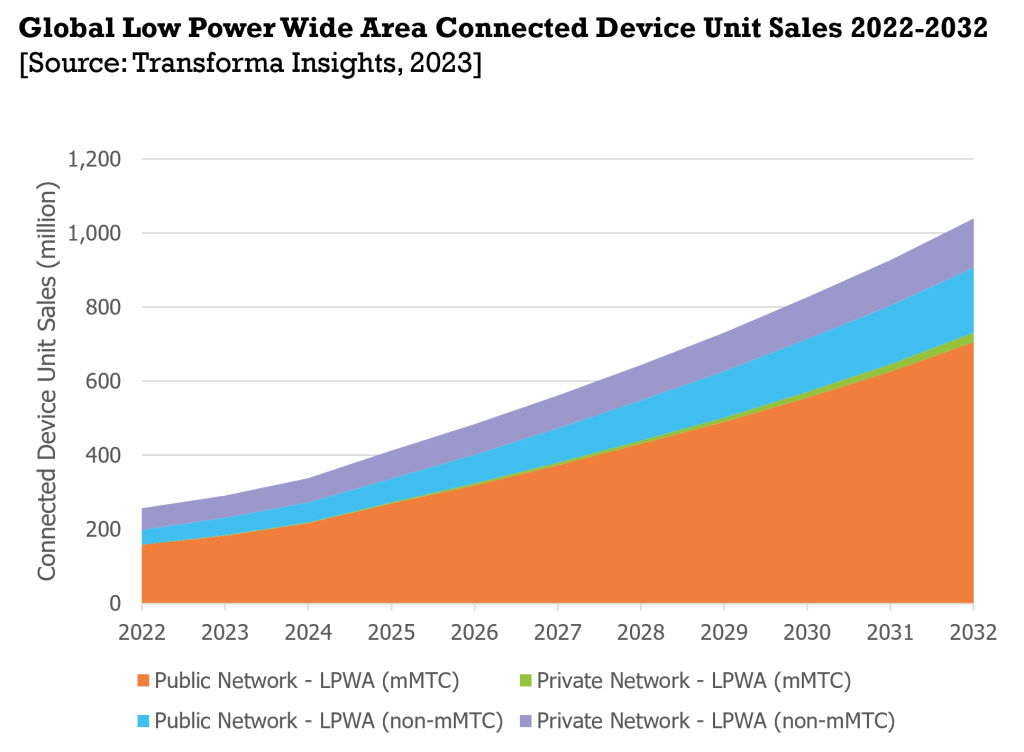
According to research from Transforma Insights, low-power mMTC devices are expected to experience a 15 percent increase in sales between 2022 and 2032, making them an ideal choice for IoT applications in asset tracking, smart cities, manufacturing, and agriculture.
Narrowband-Internet of Things (NB-IoT)
Narrowband-IoT (NB-IoT) is a 3GPP-Standardised LPWAN protocol that connects static devices over unused frequency bands in cellular networks. NB-IoT is designed for cellular machine-to-machine M2M communications and is better for low data-rate applications than other LTE technology.
NB-IoT improves the power efficiency of networked devices and can support multiple years of battery life. It is designed for large-scale IoT deployments where sensors are static and continuous cellular coverage is critical. Many vendors support NB-IoT technology and aren’t dominantly controlled by a single player; this gives enterprises across multiple sectors the flexibility to deploy at scale.
LTE-M
Yet another cellular LPWAN technology developed for IoT applications that connect directly to a 4G network via eSIM. LTE-M lends better for IoT use cases requiring higher bandwidth and lower latency than the NB-IoT use case.
LTE-M devices are inexpensive to buy and have extended battery life. Devices connected over LTE-M can enter “Power Savings Mode,” allowing batteries to last up to ten years. LTE-M is ideal for simple asset tracking of vehicles or containers for devices that don’t need a fixed power supply. It is also a good choice for static devices such as smart meters.
Subscription Costs
Subscription costs are based on the network type, data bandwidth, and roaming needs. eSIM can help manage subscription costs by allowing the “localization” of a device to a local MNO profile to reduce expensive roaming costs.
Tweet
Share
Share
- Cellular
- Connectivity
- eSIM
- LPWAN
- NB-IoT
- Cellular
- Connectivity
- eSIM
- LPWAN
- NB-IoT
