In today’s digital age, maintaining uninterrupted data connectivity is paramount as both businesses and individuals rely on a continuous flow of information. This reliability is crucial as it ensures that critical operations and services remain accessible without any disruptions, and MQTT and Inter-broker Communication can play a vital role.
To achieve this level of resilience, we can deploy an MQTT cluster setup where each broker serves as a master. This reduces the dependency on conventional master-slave architecture.
Let’s delve into this topic by examining its key building blocks.
MQTT Broker: A Closer Look
An MQTT broker serves as a central communication hub within the Internet of Things (IoT). Its primary function is to ease data exchange between connected devices.
It receives messages from devices, known as publishers and ensures the delivery of these messages to the correct recipients. This enables efficient and real-time communication in IoT applications.
To lay it out plain and simple, envision the MQTT broker as the diligent courier in your digital world. It shuttles messages between publishers and receivers.
For example, it facilitates sharing alerts to your mobile from your smart devices. It ensures messages find their way from sender to recipient with effectiveness.
This unseen hero orchestrates seamless communication between publishers and receivers. It guarantees precise data deliveries in the virtual realm.
High Availability: A Non-Negotiable Need
High Availability (HA) ensures uninterrupted operations even in the face of failures. A high availability feature is necessary for MQTT brokers to ensure seamless communication between the devices.
Elevating the availability of MQTT brokers is inevitable. It’s essential to eradicate the downtime for enterprise-grade performance. High availability serves as a guardian. It ensures the clients never encounter a locked door when reaching out to the broker.
An HA setup distributes the incoming MQTT traffic between several MQTT brokers. This action prevents the overloading of a single broker. This in turn enhances the performance and ensures seamless transmission of data.
It safeguards against various forms of failures. It also supports the scalability needs of modern IoT and messaging systems.
Active-Active vs. Active-Passive Mechanism
There are two distinct modes of high availability clustered setup: active-active and active-passive mechanisms.
Let’s scrutinize the dissimilarities between both mechanisms.
Active-Active
The Active-Active mechanism involves setting up a cluster with 2 or more MQTT brokers. Every broker in this setup remains active. The cluster’s primary purpose is to enhance load balancing.
It achieves this by distributing data across all available brokers. This approach ensures that no single broker becomes overloaded.
Active-Passive
In contrast, the Active-Passive mechanism is also a clustered setup. But not all brokers within it are active. There are two brokers in this configuration.
One is active, while the other remains in standby mode. When an issue arises with the active broker, the standby broker steps in. This ensures the continuous flow of data without any disruptions.
In essence, active-active mechanisms resemble an orchestrated symphony of efficiency. All components work in harmony to ensure uninterrupted performance.
Active-active setups maintain constant service flow, while active-passive setups rely on passive standby. They also maintain a harmonious operation. This enhances both availability and responsiveness.
Inter-Broker Communicator (IBC) in a Nutshell
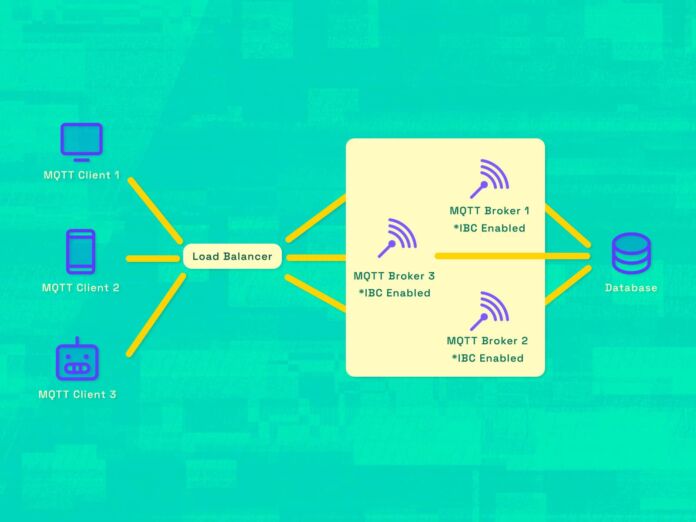
Take a look at the following example. It illuminates the approach to achieving high availability. This approach involves several MQTT brokers with Inter-broker Communication enabled.
This Inter-broker Communication functions as a bridge and connects all brokers within the MQTT broker cluster. It ensures uninterrupted bidirectional communication with devices. This remains consistent regardless of the specific broker clients choose to connect to.

In this, two or more MQTT brokers with IBC collaboration form a clustered setup. The pivotal player joining them is the load balancer.
This load balancer plays a starring role in the show by managing incoming connections to the broker nodes. In this active-active mode, the load balancer doesn’t wait for a broker to falter. It directs connections to all active nodes without delay.
In the event of a broker hiccup, the load balancer switches gears. It ceases connections to the affected broker & reallocates them to the unaffected ones.
This decision-making process factors in performance and designated weightage. It ensures the system’s orchestration is always tuned for uninterrupted performance.
Within the architecture of MQTT brokers, the Inter-Broker Communicator (IBC) takes center stage. It acts as a vital component.
IBC serves the crucial function of facilitating seamless communication among MQTT broker instances. Moreover, it coordinates these instances within a clustered MQTT system.
IBC’s Significance: Why it Counts
One of the primary roles of IBC is to enable MQTT brokers to share essential information. This information concerns client connections, topics, and message queues across the entire broker cluster.
Despite the connected broker, the IBC ensures access to the client’s data and messages. It also guarantees transparent delivery.
Additionally, the IBC is pivotal in load balancing within the active-active setup. When an MQTT broker in the cluster overloads or fails, the Inter-broker Communication steps in.
It redirects client connections to other available brokers in the setup. This dynamic load-balancing strategy ensures that no single broker becomes overwhelmed. It also helps optimize the use of system resources, enhancing performance and responsiveness.
Fusion of Mechanisms
The fusion of active-active mechanisms and Inter-broker Communication in the MQTT broker is crucial. This ensures uninterrupted data connectivity as every second counts in the digital realm.
These resilient configurations serve as guardians of seamless operations. They enable access to critical services without a hitch and their role is to accelerate efficiency and protect against disruptions. They are tailored to meet the relentless demands of our fast-paced, digitally-driven world.
Tweet
Share
Share
- Data Analytics
- MQTT
- Network and Protocols
- Data Analytics
- MQTT
- Network and Protocols
